Top Portfolio Management Best Practices for 2025
If a stock moves past your strike, the option can be assigned — meaning you'll have to sell (in a call) or buy (in a put). Knowing the assignment probability ahead of time is key to managing risk.
Posted by
Related reading
Mastering Option Extrinsic Value
Unlock the core of options trading by mastering option extrinsic value. Learn how time, volatility, and strategy impact your profits with this guide.
A Trader's Guide to Short Put Options
Discover how to use short put options to generate consistent income or buy stocks at a lower price. This guide covers key strategies and risk management.
8 Best Stocks for Put Selling in 2025
Discover the best stocks for put selling to generate consistent income. Our guide breaks down top picks, key metrics, and actionable strategies for success.
Successful options trading isn't just about picking the right strike or expiry date; it’s about holistically managing your entire portfolio to generate consistent income while protecting capital. Many traders focus intensely on individual trades, like the perfect covered call or cash-secured put, but neglect the overarching strategies that separate amateur speculators from professional income generators. This oversight can lead to concentrated risk, missed opportunities, and a portfolio that's vulnerable to market swings.
This guide moves beyond individual trade mechanics to reveal the essential portfolio management best practices that empower sophisticated options sellers. We will explore 10 proven strategies, from advanced diversification techniques tailored for options to disciplined risk management frameworks that ensure long-term success. By integrating these practices, you can transform your trading from a series of isolated bets into a cohesive, strategic, and profitable operation.
These concepts are fundamental for building a resilient, income-focused portfolio. We will provide actionable steps and real-world examples to help you implement these principles effectively. The goal is to move beyond short-term wins and establish a durable system for consistent returns, turning complex portfolio management into a streamlined, repeatable process.
1. Diversification Across Multiple Asset Classes
At its core, strategic diversification is the practice of spreading investments across various financial instruments and asset classes to reduce risk. This fundamental principle, a cornerstone of Modern Portfolio Theory, ensures that a downturn in one area doesn't disproportionately harm your entire portfolio. It's one of the most crucial portfolio management best practices for building resilience.
Why It Works
By combining assets with low or negative correlations, such as stocks, bonds, and alternatives, you can smooth out returns. For instance, when stocks fall during an economic downturn, high-quality government bonds often rise, balancing out potential losses. This approach was famously implemented by David Swensen at the Yale Endowment, which achieved remarkable long-term returns by allocating significantly to alternative investments like private equity and real assets.
For options traders, a diversified underlying portfolio provides a stable foundation, reducing the systemic risk that could otherwise jeopardize premium-generating strategies. For a comprehensive approach to mitigating risk and optimizing returns, consider exploring these 9 Essential Investment Diversification Strategies.
This infographic summarizes the core components of a diversified portfolio.
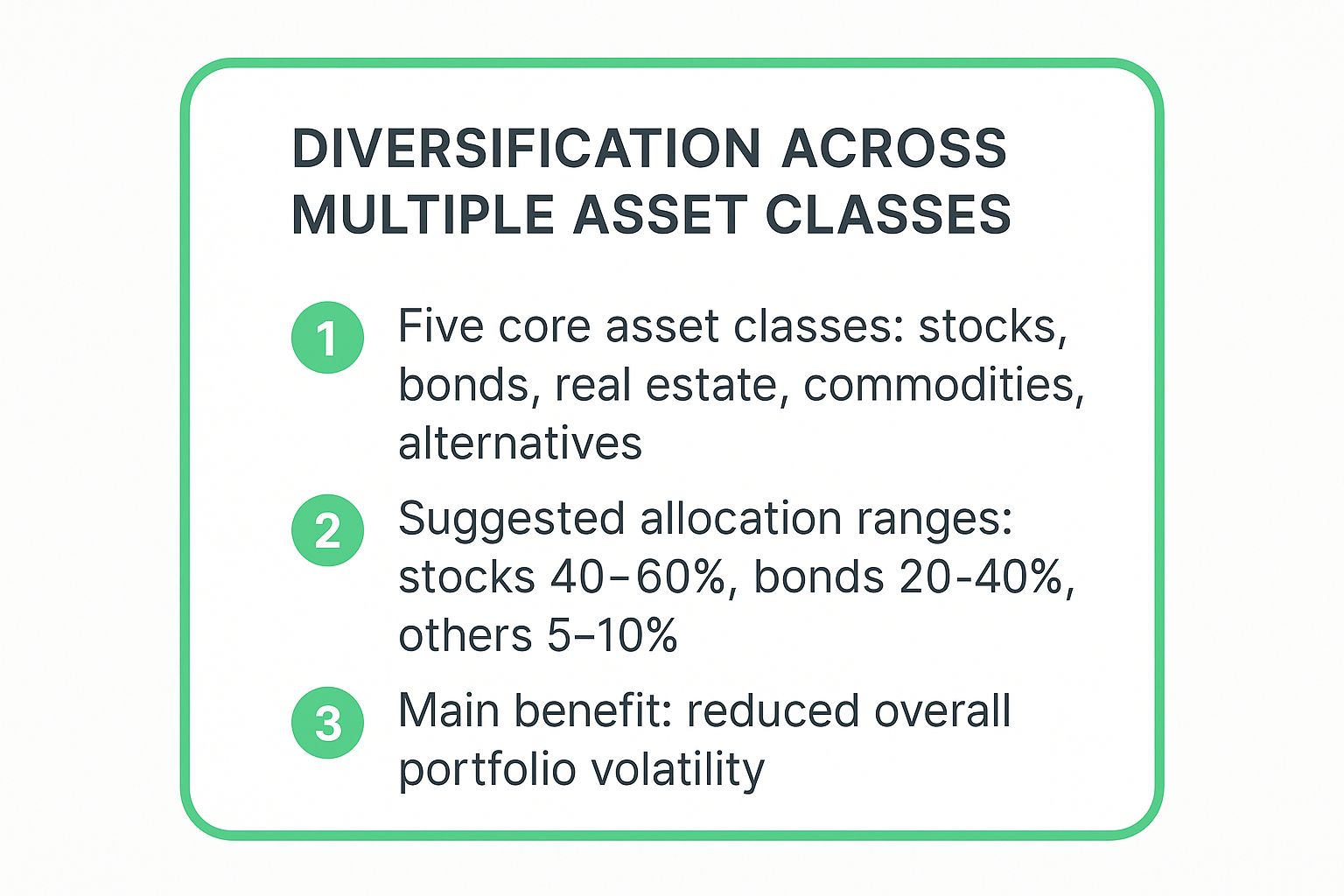
As the data highlights, allocating capital across these distinct categories helps stabilize your portfolio's value against the volatility of any single market segment.
Actionable Tips
- Review Correlations: Check the correlation matrix of your holdings quarterly to ensure your assets are not moving in lockstep.
- Utilize Index Funds: Gain broad, low-cost exposure to entire markets like the S&P 500 or global bonds through ETFs or index funds.
- Avoid Over-Diversification: Owning too many assets can dilute returns and make the portfolio difficult to manage effectively. Aim for targeted, meaningful positions.
2. Regular Portfolio Rebalancing
Regular rebalancing is the systematic process of realigning your portfolio's asset weightings back to their original targets. Over time, market movements cause some assets to grow faster than others, drifting your allocation away from its intended risk profile. This disciplined approach is a critical portfolio management best practices for managing risk and capturing gains.
This chart illustrates how an unbalanced portfolio can drift from its target allocation, exposing an investor to unintended risks over time.

By regularly selling overperforming assets and buying underperforming ones, you systematically "sell high and buy low," maintaining alignment with your long-term investment goals.
Why It Works
Rebalancing enforces investment discipline and prevents emotional decision-making. Ray Dalio’s "All Weather" strategy at Bridgewater Associates heavily relies on systematic rebalancing to maintain its risk-parity structure, ensuring stability across different economic environments. Similarly, large institutions like CalPERS rebalance consistently to stay on track toward their target returns.
For options traders, a well-balanced portfolio provides a stable collateral base, preventing overallocations to volatile assets that could increase the risk of margin calls. A detailed guide can help you master this technique; discover more about how to rebalance your portfolio effectively.
Actionable Tips
- Set Tolerance Bands: Instead of rebalancing on a fixed schedule, rebalance only when an asset class drifts by a predetermined amount, such as ±5% from its target.
- Use New Capital: Rebalance by directing new contributions to underweighted asset classes. This minimizes transaction costs and potential tax liabilities from selling appreciated assets.
- Consider Tax Implications: When selling assets in a taxable account, look for opportunities for tax-loss harvesting to offset gains.
3. Strategic Asset Allocation Based on Goals
Strategic asset allocation is a disciplined, long-term approach where you set target percentages for different asset classes based on your financial goals, time horizon, and risk tolerance. Rather than reacting to short-term market noise, this method creates a stable framework that guides all investment decisions. This is one of the most foundational portfolio management best practices for achieving consistent, goal-oriented results.
Why It Works
This strategy anchors your portfolio to your personal objectives, preventing emotional decision-making during market volatility. It enforces a buy-low, sell-high discipline through rebalancing. For instance, a young investor's portfolio might be allocated 90% to stocks and 10% to bonds, while a retiree's might be 40% stocks and 60% bonds. This structure was championed by figures like David Swensen at the Yale Endowment, who used a clear allocation model to drive exceptional long-term growth.
For options traders, a defined asset allocation provides a stable capital base from which to generate income, ensuring that riskier strategies do not compromise core financial goals. To build this foundation effectively, it is essential to first understand how to set clear financial goals.
Actionable Tips
- Create an Investment Policy Statement (IPS): Formally document your goals, risk tolerance, and target allocations to maintain discipline.
- Use Age-Based Rules as a Guide: Start with a simple rule like "100 minus your age" to determine your stock allocation percentage, then adjust for your specific risk profile.
- Review and Rebalance Periodically: Check your allocations annually or after major life events (marriage, new job) to ensure they still align with your goals, and rebalance back to your target weights.
4. Risk management and Position Sizing
Effective risk management is a disciplined, systematic approach to controlling portfolio risk through appropriate position sizing and loss mitigation. It ensures that no single investment or trade can inflict catastrophic damage on your overall portfolio. This is one of the most vital portfolio management best practices because it prioritizes capital preservation above all else.

This practice is essential for options traders, where leverage can amplify both gains and losses. Understanding how to manage risk is the difference between sustainable income generation and a blown-up account. To delve deeper into this critical topic, you can explore these essential options trading risk management techniques.
Why It Works
By predefining the maximum acceptable loss for any single position, you cap your downside. Legendary investors like Ed Thorp applied rigorous mathematical models to manage risk, ensuring long-term survival and profitability. Similarly, Ray Dalio’s risk parity strategy equalizes the risk contribution from each asset class, preventing over-concentration. This methodical approach removes emotion from decision-making, forcing discipline during market turmoil.
For option sellers, this means calculating the maximum potential loss on a cash-secured put or a defined-risk spread before entering the trade and sizing the position accordingly.
Actionable Tips
- Implement a Sizing Rule: Adhere to a strict rule, such as never risking more than 2% of your portfolio's capital on a single trade.
- Set Concentration Limits: Avoid over-allocating to a single stock or sector. For example, limit any single equity position to no more than 5-10% of your total portfolio value.
- Use Protective Options: Employ strategies like buying protective puts or using collars to hedge downside risk on core equity holdings, especially during volatile periods.
5. Cost Minimization and Fee Management
Every dollar paid in fees is a dollar that isn't compounding for you. Cost minimization is the systematic practice of reducing investment expenses, including transaction fees, expense ratios, and tax implications, to maximize net returns. This disciplined approach is a cornerstone of effective portfolio management best practices, as even small, seemingly insignificant fees can dramatically erode wealth over time.
This infographic highlights the long-term impact of high fees on portfolio growth.

As the data shows, minimizing these costs directly translates to higher accumulated capital over an investment horizon.
Why It Works
The power of cost minimization lies in the certainty of its impact. While market returns are unpredictable, fees are a constant drag on performance. Vanguard founder Jack Bogle famously demonstrated that a low-cost index fund could generate significantly more wealth over decades compared to a high-fee active fund with identical gross returns. By keeping costs low, more of your capital remains invested and continues working for you, enhancing the effects of compounding.
For options traders, high transaction fees can quickly consume the premium collected from strategies like covered calls or cash-secured puts. A low-cost brokerage is essential for preserving profitability.
Actionable Tips
- Target Low Expense Ratios: Aim for broad-market index funds and ETFs with expense ratios below 0.20% to keep foundational costs minimal.
- Leverage Tax-Advantaged Accounts: Place tax-inefficient assets, like actively traded options or high-turnover funds, within accounts like an IRA or 401(k) to defer or eliminate taxes on gains.
- Compare All-In Costs: Look beyond the expense ratio to understand all potential fees, including trading commissions, bid-ask spreads, and account maintenance charges.
6. Tax-Efficient Investment Strategies
A crucial component of maximizing returns is minimizing the drag from taxes. Tax-efficient investment strategies involve a deliberate approach to structuring your portfolio to reduce tax liability. This goes beyond simple tax filing and is one of the most impactful portfolio management best practices for preserving long-term wealth, as it directly increases your after-tax returns.
Why It Works
This practice works by strategically using tax-advantaged accounts, optimizing asset location, and managing holding periods. For instance, placing high-turnover or income-generating assets like REITs and actively traded options in tax-deferred accounts (like an IRA or 401(k)) shields them from annual taxation. Conversely, assets with long-term capital gains potential, like growth stocks, are better suited for taxable accounts where they can benefit from lower tax rates. The research of financial experts like William Reichenstein has consistently shown that proper asset location alone can add significant value over an investor’s lifetime.
For options traders, understanding the tax implications of short-term versus long-term gains (Section 1256 contracts) is critical for strategy selection and timing. Tax-loss harvesting, where losing positions are sold to offset gains, further enhances after-tax performance.
Actionable Tips
- Prioritize Tax-Advantaged Accounts: Maximize your annual contributions to your 401(k), IRA, and other tax-sheltered accounts before investing heavily in a taxable brokerage account.
- Optimize Asset Location: Hold tax-inefficient assets (e.g., corporate bonds, REITs) in retirement accounts and tax-efficient assets (e.g., index funds, municipal bonds) in taxable accounts.
- Harvest Losses Systematically: Regularly review your portfolio for opportunities to realize losses to offset capital gains, being mindful of the wash-sale rule.
- Manage Holding Periods: Aim to hold appreciative assets for over one year in taxable accounts to qualify for more favorable long-term capital gains tax rates.
7. Performance Monitoring and Benchmarking
Systematic performance monitoring is the practice of tracking and evaluating your portfolio against relevant benchmarks and stated objectives. This process provides an objective assessment of your investment success, highlights strategic drift, and identifies areas for improvement. It is one of the most vital portfolio management best practices for ensuring your strategy remains on track.
Why It Works
By comparing your returns to a suitable benchmark, you can determine if your strategy is generating alpha or simply riding market trends. Pioneers like William Sharpe, with his risk-adjusted return metric (the Sharpe Ratio), provided the framework for this analysis. For example, the California Public Employees' Retirement System (CalPERS) publishes detailed reports showing its performance against custom benchmarks, creating accountability and clarity. This disciplined approach prevents emotional decision-making and keeps your actions aligned with your long-term goals.
For an options trader, benchmarking an income-focused portfolio against an index like the Cboe S&P 500 BuyWrite Index (BXM) can validate the effectiveness of a covered call strategy. It answers the critical question: "Is my active management adding value?"
This data table illustrates how different benchmarks align with specific strategies.
| Portfolio Strategy | Relevant Benchmark Example | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| U.S. Large-Cap Equity | S&P 500 Index | Measures performance against the broad U.S. large-cap market. |
| Global Diversified | MSCI ACWI Index | Provides a benchmark for portfolios with global stock exposure. |
| Options Income (Covered Call) | Cboe S&P 500 BuyWrite Index (BXM) | Tracks the performance of a hypothetical covered call strategy. |
| High-Yield Corporate Bonds | Bloomberg U.S. Corporate High Yield Bond Index | Compares performance to the high-yield bond market. |
As the data shows, selecting the right benchmark is crucial for a meaningful performance comparison.
Actionable Tips
- Choose Relevant Benchmarks: Your benchmark should match your portfolio's asset allocation and risk profile, not just a popular index like the S&P 500.
- Focus on Risk-Adjusted Returns: Use metrics like the Sharpe Ratio to evaluate performance, as high returns accompanied by excessive risk may not be sustainable.
- Evaluate Over Full Market Cycles: Assess performance over at least a 3-5 year period to avoid drawing conclusions from short-term market noise.
8. Long-term Investment Horizon Discipline
Adopting a long-term investment horizon is about prioritizing sustained wealth creation over chasing short-term market fluctuations. This discipline involves resisting emotional reactions to market noise and staying committed to a well-defined strategy, allowing the power of compounding to work its magic. It is one of the most foundational portfolio management best practices for achieving meaningful growth.
Why It Works
By focusing on "time in the market, not timing the market," you avoid the common pitfalls of trying to predict market movements, a strategy that often leads to buying high and selling low. A long-term view leverages compound growth and smooths out volatility. Warren Buffett’s Berkshire Hathaway exemplifies this, having held Coca-Cola since 1988 and realizing returns exceeding 1,600%. This "stay the course" philosophy helps investors capture the market's historical upward trend.
For options traders, this long-term discipline provides a stable, appreciating underlying portfolio. This foundation generates a reliable base from which to sell calls or secure puts, ensuring that short-term premium generation activities support, rather than detract from, the primary goal of long-term capital appreciation.
Actionable Tips
- Create an Investment Policy Statement: Write down your financial goals, risk tolerance, and long-term strategy. Refer to it during market turmoil to maintain discipline.
- Automate Your Investments: Set up automatic, recurring contributions to your portfolio. This removes emotion and ensures you consistently invest through market cycles.
- Focus on Annual Reviews: Review your portfolio and goals once a year, not every day. This prevents knee-jerk reactions to temporary market downturns.
9. Liquidity Management and Cash Allocation
Effective liquidity management involves strategically holding cash and near-cash assets to cover short-term obligations, seize unexpected opportunities, and provide a buffer during market downturns. This practice balances the need for accessible funds with the goal of optimizing returns. It's a foundational component of sound portfolio management best practices that ensures financial stability and flexibility.
Why It Works
Holding "dry powder" allows an investor to act decisively when markets present bargains, a concept championed by investors like Seth Klarman and Howard Marks. For options traders, maintaining adequate cash is non-negotiable for covering potential assignments on short puts or meeting margin requirements. This prevents forced selling of long-term holdings at inopportune times. For example, a company like Apple historically maintains a massive cash reserve, giving it immense strategic flexibility for acquisitions, R&D, or weathering economic shocks.
This approach acts as a crucial safety net, ensuring you have the resources to manage obligations and capitalize on volatility without disrupting your core investment strategy.
Actionable Tips
- Establish an Emergency Fund: Keep 3-6 months of living expenses in a high-yield savings account or a money market fund, completely separate from your investment portfolio.
- Allocate for Opportunities: Set aside 5-10% of your investment portfolio in cash or cash equivalents to deploy during market corrections or for new opportunities.
- Plan for Known Expenses: Use tools like short-term CD ladders to prepare for predictable future expenses, such as taxes or a down payment, ensuring the cash is available when needed.
10. Regular Investment Education and Staying Informed
The financial markets are not static; they evolve with economic shifts, technological advancements, and changing investor sentiment. Committing to continuous learning is a fundamental portfolio management best practice that separates successful investors from the rest. It involves staying current on market developments, new strategies, and timeless investment principles to make more informed decisions.
Why It Works
Continuous education equips you to adapt your strategies and avoid costly mistakes driven by outdated assumptions. Legends like Warren Buffett and Charlie Munger attribute much of their success to their voracious reading and multidisciplinary approach to learning. By understanding the "why" behind market movements and strategy mechanics, you can better navigate volatility and identify opportunities that others might miss. This proactive learning builds the conviction needed to stick with a sound strategy during turbulent times.
For options traders, staying informed about changes in implied volatility, sector news, or new derivative products is critical. A deeper understanding of market dynamics allows for more precise strategy selection and risk management, turning theoretical knowledge into tangible portfolio gains.
Actionable Tips
- Establish a Reading Habit: Dedicate time each week to read quality financial publications, company annual reports, and investment books.
- Focus on Principles, Not Predictions: Prioritize learning timeless concepts like valuation, risk management, and investor psychology over trying to guess short-term market moves.
- Seek Diverse Perspectives: Actively look for well-reasoned arguments that challenge your own beliefs to avoid confirmation bias and strengthen your investment thesis.
- Apply Learnings Gradually: When you learn a new concept or strategy, test it with a small portion of your capital before making any dramatic shifts to your overall portfolio.
Portfolio Management Best Practices Comparison
| Strategy | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diversification Across Multiple Asset Classes | Medium - requires correlation and geographic analysis | Moderate - multiple assets, monitoring | Reduced portfolio volatility, downside protection | Long-term investors seeking risk reduction | Minimizes concentration risk, broad growth opportunities |
| Regular Portfolio Rebalancing | Medium - systematic process, frequency based | Moderate - transaction costs, automated tools | Maintains target allocation, enforces discipline | Investors needing disciplined allocation maintenance | Prevents drift, enforces buy-low/sell-high behavior |
| Strategic Asset Allocation Based on Goals | Medium - goal and risk assessment based | Moderate - requires review and customization | Alignment with financial goals, reduces emotional decisions | All investor types with clear objectives | Provides clear decision framework, systematic wealth build |
| Risk Management and Position Sizing | High - requires quantitative analysis and rules | High - risk metrics, tools for monitoring | Limits losses, improves consistent returns | Risk-averse investors and professional traders | Prevents catastrophic losses, quantitative risk control |
| Cost Minimization and Fee Management | Low to Medium - ongoing fee monitoring | Low to Moderate - research and monitoring | Improved net returns over time | Cost-conscious investors | Significantly boosts long-term returns via fee control |
| Tax-Efficient Investment Strategies | Medium to High - complex tax rules and account optimization | Moderate to High - requires tax knowledge and tracking | Maximizes after-tax returns | Investors in taxable accounts, retirement planners | Enhances net returns through tax strategies |
| Performance Monitoring and Benchmarking | Medium - requires sophisticated analysis tools | Moderate - time investment in tracking | Objective performance evaluation | Investors wanting data-driven insights | Identifies success and failure, supports accountability |
| Long-term Investment Horizon Discipline | Low - behavior and mindset focused | Low - emphasis on discipline rather than tools | Maximized compound growth, reduced costs | Investors with long-term goals | Simplifies process, reduces emotional decisions |
| Liquidity Management and Cash Allocation | Medium - balancing cash needs and investment returns | Moderate - managing liquid assets | Financial security, opportunity readiness | Investors needing short-term liquidity | Prevents forced sales, maintains stability |
| Regular Investment Education and Staying Informed | Medium - continuous time commitment | Low to Moderate - time and access to resources | Enhanced decision-making, adaptability | All investors aiming to improve knowledge | Builds confidence, keeps pace with market evolution |
Integrating Best Practices into a Cohesive Strategy
Navigating the world of options trading without a structured framework is like sailing without a compass. The ten portfolio management best practices detailed in this guide provide that essential direction, transforming sporadic trades into a disciplined, wealth-building engine. Moving beyond a myopic focus on individual trades is the most critical shift an investor can make. It's about building a resilient system where every decision supports your overarching financial goals.
The principles we've explored, from strategic diversification and disciplined rebalancing to meticulous risk management and tax efficiency, are not isolated tactics. They are interconnected pillars that support the entire structure of your investment portfolio. For an options seller, this means evaluating a new covered call not just on its premium, but on how it affects your sector allocation, overall portfolio delta, and liquidity position. True mastery comes from integrating these concepts into a seamless, repeatable process.
From Theory to Actionable Implementation
The value of these principles lies in their consistent application. This is where many investors falter, getting lost in the complexity of tracking multiple positions, calculating risk metrics, and staying aligned with long-term objectives.
Here are the key takeaways to turn these best practices into habits:
- Adopt a Portfolio-Centric View: Before entering any new options trade, ask: "How does this position impact my total portfolio?" Consider its effect on diversification, risk exposure, and your target return profile.
- Systematize Your Review Process: Schedule regular check-ins, perhaps monthly or quarterly, to rebalance, review performance against benchmarks, and ensure your asset allocation still aligns with your goals and risk tolerance.
- Leverage Technology: Manually tracking every variable is inefficient and prone to error. Modern tools can automate the heavy lifting of performance monitoring, risk analysis, and opportunity identification, allowing you to focus on high-level strategy. This systematic approach is a cornerstone of effective portfolio management.
The Broader Impact on Your Financial Future
Ultimately, implementing these portfolio management best practices is about more than just improving your returns; it's about gaining control, reducing stress, and building sustainable, long-term wealth. A well-managed portfolio can withstand market volatility, minimize costly mistakes, and compound more effectively over time. While our focus has been on trading securities, these principles are universal. To truly elevate your investment strategy, it is crucial to integrate comprehensive asset management best practices into your overall plan, especially if you hold other assets like real estate. By combining timeless investment wisdom with data-driven execution, you elevate your options strategy from a speculative venture to a disciplined, income-generating business.
Ready to implement these portfolio management best practices with precision and ease? Strike Price provides a unified dashboard to monitor your positions, track income goals, and analyze risk in real-time. Stop guessing and start managing your options portfolio like a professional with a free 14-day trial of Strike Price today.