6 Credit Put Spread Example Trades for 2025
If a stock moves past your strike, the option can be assigned — meaning you'll have to sell (in a call) or buy (in a put). Knowing the assignment probability ahead of time is key to managing risk.
Posted by
Related reading
A Step-by-Step Covered Calls Example for Consistent Income
Unlock consistent income with our step-by-step covered calls example. This guide breaks down the strategy, risks, and outcomes to help you trade confidently.
Long Call and Short Put The Ultimate Synthetic Stock Guide
Unlock the power of the long call and short put strategy. This guide explains how synthetic long stock works, its benefits, risks, and how to execute it.
What is a Call Spread? A Clear Guide to Bull and Bear Spreads
What is a call spread? Discover how bull and bear spreads limit risk and sharpen your options trading strategy.
The credit put spread is a cornerstone strategy for options traders seeking consistent income, but moving from textbook definitions to real-world application is where many stumble. The goal isn't just to understand the mechanics; it's to see how the strategy performs under different market conditions, with various underlying assets, and across multiple timeframes. This guide bridges that gap by providing a detailed breakdown of the strategy in action.
We will dissect six distinct credit put spread example scenarios, detailing the exact trade setup, the strategic reasoning behind strike selection, risk management protocols, and the final outcomes. From navigating the high liquidity of an SPY monthly trade to harnessing the volatility of Tesla, each case study provides a replicable blueprint to help you trade with greater confidence and precision.
You will learn not just what was traded but why a particular setup made sense in that specific context. This article moves beyond theory, empowering you with the tactical insights and practical applications needed to successfully implement this powerful income-generating strategy in your own portfolio. We'll explore diverse examples, including trades on Apple (AAPL), Microsoft (MSFT) during earnings, and broad market ETFs like QQQ and IWM.
1. SPY Credit Put Spread (Monthly)
The SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY) is a foundational asset for many options traders, making it an ideal candidate for our first credit put spread example. This strategy involves selling a put option and buying a further out-of-the-money put option with the same expiration date. The goal is to collect a premium, known as the credit, and profit as long as SPY's price stays above the higher strike price of the sold put at expiration.
This approach is popular due to SPY's high liquidity, tight bid-ask spreads, and its tendency to follow a general long-term upward trend. A trader using this strategy is moderately bullish to neutral on the market over the next 30-45 days. They believe SPY will either rise, stay flat, or only fall slightly, allowing the options to expire worthless and letting them keep the full credit.
Trade Setup and Rationale
A common approach involves selecting strikes based on delta, which represents the probability of an option finishing in-the-money. Traders often sell a put with a delta between 0.15 and 0.35, giving them a high probability of success.
Here is a common credit put spread example using SPY:
- Action: Sell 1 SPY $450 Put
- Action: Buy 1 SPY $445 Put
- Expiration: 30 days out
- Net Credit: $2.00 per share ($200 per contract)
In this case, the maximum profit is the $200 credit received upfront. The maximum loss is the difference between the strikes ($5) minus the credit ($2), resulting in a $300 risk per contract. The break-even point is the short strike minus the credit ($450 - $2 = $448). As long as SPY closes above $448 at expiration, the trade is profitable.
The following infographic highlights the key parameters for structuring a typical SPY credit put spread.
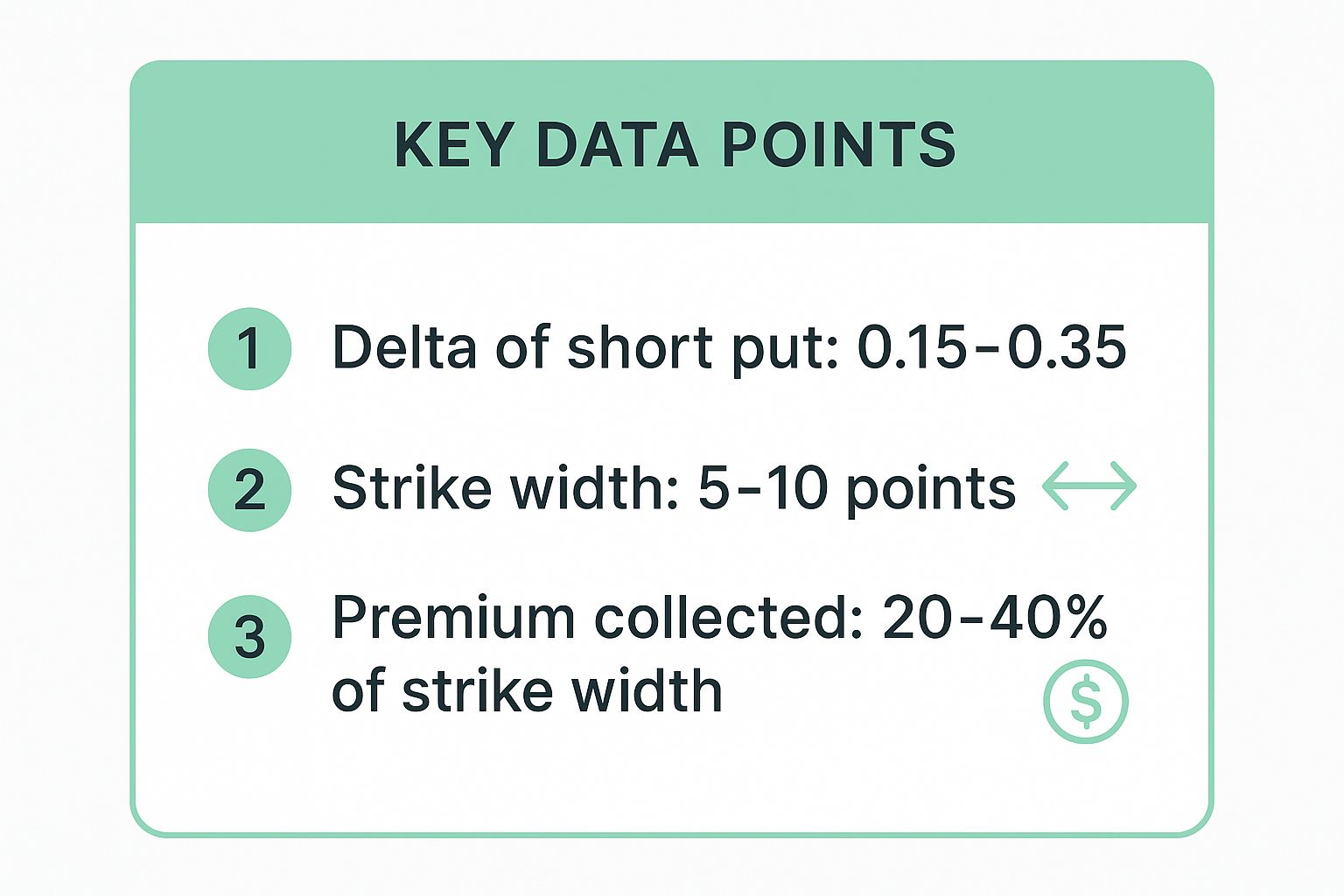
These metrics provide a solid framework for building a high-probability trade that balances risk and potential reward effectively.
Actionable Takeaways
To effectively implement this strategy, consider the following tactical advice:
- Optimal Timeframe: Open positions 30-45 days from expiration (DTE) to maximize the rate of time decay (theta).
- Profit Target: Don't wait until expiration. A good practice is to close the trade when you've captured 50% of the maximum profit. This reduces risk exposure.
- Risk Management: Size your position appropriately. Never risk more than 1-2% of your total portfolio value on a single trade.
- Market Conditions: This strategy performs best in neutral to bullish markets. Avoid opening new spreads when market volatility, measured by the VIX index, is excessively high (e.g., above 25-30), as sharp price swings can quickly turn a winning trade into a loser.
2. Apple (AAPL) Weekly Credit Put Spread
Apple Inc. (AAPL) is a favorite among options traders due to its massive liquidity, tight bid-ask spreads, and generally stable price action supported by strong fundamentals and institutional buying. A weekly credit put spread on AAPL is a short-term strategy designed to generate income by taking advantage of its tendency to hold key support levels over a few trading days. The goal is to collect a premium, betting that AAPL will remain above a specific price by the end of the week.
This approach is best suited for traders with a neutral to slightly bullish short-term outlook on the stock. By using weekly options, traders can accelerate time decay (theta) and potentially compound returns more frequently. This strategy leverages Apple's high options volume, ensuring that entering and exiting trades is efficient.

Trade Setup and Rationale
A common weekly strategy involves opening a trade on Monday or Tuesday and targeting an expiration for that Friday. Traders often select the short strike price based on a recent support level identified through technical analysis, giving the position a buffer against minor price drops.
Here is a typical credit put spread example using weekly AAPL options:
- Action: Sell 1 AAPL $145 Weekly Put
- Action: Buy 1 AAPL $142.50 Weekly Put
- Expiration: 4 days out (e.g., entered Monday, expires Friday)
- Net Credit: $0.75 per share ($75 per contract)
In this scenario, the maximum profit is the $75 credit. The maximum loss is the width of the strikes ($2.50) minus the credit ($0.75), which equals $1.75 per share, or $175 per contract. The break-even point is the short strike minus the credit ($145 - $0.75 = $144.25). The trade is profitable if AAPL closes above $144.25 at the week's end. This strategy works well during periods of positive sentiment, like the weeks surrounding an iPhone launch, but can incur losses during broad market downturns, such as the tech selloff in early 2022.
Actionable Takeaways
To effectively implement this short-term strategy on AAPL, consider these key tactics:
- Optimal Entry: Open positions on a Monday or Tuesday to allow time decay to work in your favor without holding risk over the weekend.
- Profit Target: A key to success with weeklies is managing trades actively. Aim to close the position early if you capture 50% of the maximum profit, especially if achieved by Wednesday or Thursday.
- Risk Management: Absolutely avoid holding this type of spread through an earnings announcement. The implied volatility crush can be tempting, but a negative earnings surprise can lead to a maximum loss instantly.
- Technical Analysis: Use technical indicators like moving averages or recent price floors to identify strong support levels. Placing your short strike below a confirmed support zone significantly increases your probability of success.
3. Tesla (TSLA) High IV Credit Put Spread
Tesla (TSLA) is renowned for its volatility, making it a prime candidate for credit put spreads designed to capitalize on high implied volatility (IV). This strategy involves selling a put and buying a further out-of-the-money put to collect a substantial premium when option prices are inflated due to market uncertainty or anticipated news. The goal is for the stock to remain above the short strike, allowing the options to expire worthless and the trader to keep the large credit.
This approach is attractive because high IV directly translates to richer option premiums. A trader using this strategy is moderately bullish to neutral on TSLA, betting that despite the volatility, the stock will not experience a drastic drop below their short strike price. By selling puts during periods of high IV, such as before earnings, traders can collect more income for taking on the same amount of risk.
Trade Setup and Rationale
The key is to enter these trades when IV is elevated, often indicated by an IV Rank above the 70th percentile. This suggests option premiums are historically expensive, providing a better risk-reward ratio for sellers. Given that high implied volatility is a key factor in selecting opportunities like this, it's beneficial to understand how implied volatility is calculated.
Here is a great credit put spread example on TSLA during a high IV period:
- Action: Sell 1 TSLA $800 Put
- Action: Buy 1 TSLA $780 Put
- Expiration: 40 days out
- Net Credit: $8.00 per share ($800 per contract)
In this trade, the maximum profit is the significant $800 credit. The maximum loss is the width of the strikes ($20) minus the credit ($8), resulting in a $1,200 risk. The break-even point is the short strike minus the credit ($800 - $8 = $792). As long as TSLA stays above $792 at expiration, the trade will be profitable.
The following video provides a visual walkthrough of setting up and managing a high-probability credit spread on a volatile stock like TSLA.
Actionable Takeaways
To effectively trade high IV spreads on volatile stocks like TSLA, consider these tactics:
- Entry Signal: Only open positions when IV Rank is above 70. This ensures you are being paid adequately for the risk.
- Strike Width: Consider using wider strikes (e.g., $20 or $30 wide on TSLA) to collect a larger premium, which can improve your break-even point and probability of success.
- Profit Target: High IV often collapses after an event like earnings. Close the trade for a 50% profit shortly after this "volatility crush" to lock in gains and avoid holding through further price swings. Time decay in options trading accelerates as expiration nears, but managing the trade early is key with volatile stocks.
- Risk Management: Avoid opening new spreads right before major company-specific announcements or macroeconomic events that could cause unpredictable, massive price moves.
4. QQQ Technology Sector Credit Put Spread
The Invesco QQQ Trust (QQQ), which tracks the NASDAQ-100 index, is heavily weighted towards the technology sector, making it a prime candidate for traders looking to capitalize on tech's long-term growth trends. A credit put spread on QQQ is a strategy that involves selling a put option and buying a further out-of-the-money put with the same expiration. The goal is to collect a premium by betting that the tech-heavy index will remain above a specific price level.
This strategy is effective for traders who are moderately bullish or neutral on the technology sector. They believe that technology's secular growth story will prevent a significant downturn within the trade's timeframe, allowing the options to expire worthless. The high liquidity and active trading of QQQ options make it easy to enter and exit these positions. For a deeper understanding of how these multi-leg strategies are structured, you can learn more about option spreads on strikeprice.app.
Trade Setup and Rationale
Traders often use technical analysis, such as key support levels, to select strike prices for a QQQ credit put spread. This approach aligns the trade's break-even point with a price level that has historically shown buying interest, increasing the probability of success.
Here is a common credit put spread example using QQQ during a period of market strength:
- Action: Sell 1 QQQ $350 Put
- Action: Buy 1 QQQ $340 Put
- Expiration: 45 days out
- Net Credit: $3.50 per share ($350 per contract)
In this trade, the maximum profit is the $350 credit received. The maximum risk is the difference in strikes ($10) minus the credit ($3.50), which equals $6.50, or $650 per contract. The break-even point is the short strike minus the credit ($350 - $3.50 = $346.50). The trade is profitable as long as QQQ closes above $346.50 at expiration. During the 2020-2021 bull market, this strategy provided consistent monthly income for many traders, but it faced significant challenges during the 2022 tech selloff.
Actionable Takeaways
To effectively trade QQQ credit put spreads, consider these tactical points:
- Monitor Earnings: Pay close attention to the earnings calendar for major QQQ components like Apple, Microsoft, and Amazon (the "FAANG" stocks). A negative earnings surprise from one of these giants can significantly impact the entire index.
- Check Volatility: Before entering a trade, check the VIX. While higher volatility means higher premiums, it also signals increased risk. Avoid opening new spreads when the VIX is in a state of extreme fear, as price swings can be unpredictable.
- Use Technical Levels: Select your short strike price below a significant technical support level. This adds an extra layer of defense to your position, as the market is more likely to find buyers at these prices.
- Adapt Position Size: Use smaller position sizes during uncertain or bearish market regimes. In strong, confirmed uptrends, you can consider scaling your size up, but always adhere to strict portfolio risk rules.
5. IWM Small-Cap Credit Put Spread
The iShares Russell 2000 ETF (IWM), which tracks the small-cap segment of the U.S. stock market, offers a unique opportunity for credit put spread traders. Small-cap stocks are generally more volatile than their large-cap counterparts, which translates to richer option premiums. This strategy capitalizes on that higher premium while betting on the resilience and growth potential of smaller companies, especially during economic expansions.
A trader using this strategy is moderately bullish on the small-cap sector. They believe IWM will remain stable or appreciate, often driven by positive economic data or a "risk-on" market sentiment. The higher implied volatility in IWM allows traders to sell puts further out-of-the-money for a decent credit, increasing the probability of the trade succeeding.
Trade Setup and Rationale
Given the higher volatility of IWM, traders can often use wider strikes to collect a meaningful premium, or sell puts at a lower delta while still receiving an attractive credit. This provides a larger buffer against downward price moves compared to a similar spread on a less volatile index like SPY.
Here is a classic credit put spread example using IWM during a period of small-cap strength:
- Action: Sell 1 IWM $190 Put
- Action: Buy 1 IWM $185 Put
- Expiration: 45 days out
- Net Credit: $2.25 per share ($225 per contract)
In this scenario, the maximum profit is the $225 credit. The maximum loss is calculated as the spread width ($5) minus the credit ($2.25), resulting in a risk of $275 per contract. The break-even point for this trade is the short strike price less the premium received ($190 - $2.25 = $187.75). The trade is profitable as long as IWM closes above $187.75 at expiration. The higher credit provides a more favorable risk-to-reward ratio than typically found on large-cap ETFs.
Actionable Takeaways
To effectively trade credit put spreads on IWM, consider these specific tactics:
- Monitor Economic Cycles: This strategy excels during the early to mid-stages of an economic expansion when small-cap companies tend to outperform. Keep a close watch on economic indicators like GDP growth and employment data.
- Use Wider Strikes: Leverage IWM's higher volatility. Consider using wider spreads (e.g., $5 or $10 wide) to capture more premium, which can improve your risk-reward profile and lower your break-even point.
- Manage Volatility: While high volatility means more premium, it also means more risk. Be prepared for larger price swings and consider closing the position early at a 50% profit target to lock in gains and reduce exposure. For a deeper dive into managing option positions, you can learn more about put option selling strategies on strikeprice.app.
- Be Aware of Market Sentiment: Small-cap stocks are often seen as a barometer for investor risk appetite. In a "risk-off" environment, IWM can fall faster and further than large-cap indices, so be cautious when market fear is high.
6. Microsoft (MSFT) Earnings Credit Put Spread
Trading around corporate earnings announcements offers a unique opportunity due to predictable spikes in implied volatility (IV). A Microsoft (MSFT) earnings credit put spread is a specialized strategy designed to capitalize on this phenomenon, leveraging the company's strong fundamentals and consistent performance. This approach involves selling a put spread just before an earnings release to collect an inflated premium, then benefiting from the rapid decrease in volatility, known as "volatility crush," that occurs after the news is public.
This strategy is tailored for traders who are neutral to bullish on Microsoft's prospects and believe the market's expected price move is overstated. By selling a spread, they bet that MSFT will not experience a catastrophic drop following its report. The high IV before earnings inflates option premiums, providing a larger credit and a wider break-even point than a similar trade during normal market conditions.
Trade Setup and Rationale
The key is to select strikes far enough out-of-the-money to provide a high probability of success, even if the stock reacts negatively to the earnings report. Traders typically enter the position 2-3 days before the announcement to capture the peak IV.
Here is a classic credit put spread example timed for a MSFT earnings event:
- Action: Sell 1 MSFT $280 Put
- Action: Buy 1 MSFT $275 Put
- Expiration: 3-5 days out (weekly options)
- Net Credit: $2.50 per share ($250 per contract)
In this scenario, the maximum profit is the $250 credit. The maximum risk is the spread width ($5) minus the credit ($2.50), totaling $250. The break-even point is the short strike minus the credit ($280 - $2.50 = $277.50). For instance, if a Q1 2022 cloud growth beat causes MSFT to gap up or stay flat, the options rapidly lose value, allowing for quick profit-taking. However, if Azure growth concerns trigger a sell-off below $277.50, the position would be at risk.
Actionable Takeaways
To effectively execute an earnings credit put spread on MSFT, consider these tactical points:
- Entry Timing: Enter the trade 1-3 days before the earnings announcement to harness the highest levels of implied volatility.
- Strike Selection: Choose your short strike 5-8% below the current stock price. This provides a buffer against a negative earnings reaction.
- Exit Strategy: Do not hold the position until expiration. Plan to close the trade the morning after the earnings release to capture the profit from volatility crush and avoid any further price risk.
- Fundamental Awareness: Stay informed about key Microsoft business segments, particularly its Azure cloud computing division. Analyst sentiment on Azure's growth rate often dictates the post-earnings price action.
Credit Put Spread Examples Comparison
| Strategy | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPY Credit Put Spread (Monthly) | Moderate complexity; monthly expirations | Low commissions; high liquidity | Consistent income; moderate premium | Long-term income with broad market exposure | Highly liquid; diversified exposure; steady returns |
| Apple (AAPL) Weekly Credit Put Spread | Higher complexity due to weekly timing | Frequent monitoring; higher transaction costs | Quick profits; limited premium | Short-term trades in stable price periods | Rapid profit cycles; strong company support |
| Tesla (TSLA) High IV Credit Put Spread | High complexity; needs volatility timing | Requires careful execution; wider strikes | High premium collection; rapid losses possible | Volatile periods with elevated IV | Exceptional premiums; benefits from volatility spikes |
| QQQ Technology Sector Credit Put Spread | Moderate complexity; tech sector focus | Good liquidity; tech monitoring required | Growth-aligned income; medium premium | Tech sector growth bets | Tech sector exposure; high liquidity; diversified tech |
| IWM Small-Cap Credit Put Spread | Moderate complexity; economic cycle sensitive | Moderate liquidity; economic data tracking | Higher premiums; cyclical performance impact | Economic expansions favoring small caps | Higher premiums; diversification; cyclical opportunities |
| Microsoft (MSFT) Earnings Credit Put Spread | High complexity; timing around earnings | Requires event monitoring; quarterly timing | Volatility crush post-earnings; short-term gains | Earnings plays with seasonal volatility | Predictable timing; strong fundamentals; volatility edge |
From Examples to Execution: Your Next Steps in Options Trading
Throughout this article, we’ve dissected six distinct credit put spread example scenarios, from the stable, index-based SPY trade to a high-stakes earnings play on Microsoft. The journey through these case studies reveals a powerful, unifying theme: success with credit put spreads is not about a single rigid formula but about strategic adaptation. It’s about tailoring your approach to the specific asset, market conditions, and your personal risk tolerance.
We saw how a lower-volatility ETF like QQQ calls for a different strike selection process than a high-IV stock like Tesla. The weekly Apple (AAPL) trade highlighted the rapid premium decay available in shorter timeframes, while the monthly SPY example showcased a more conservative, set-and-forget style approach. Each case was a lesson in matching the tool to the task at hand.
Synthesizing the Core Lessons
The true value of analyzing each credit put spread example lies in extracting the repeatable principles that transcend any single trade. If you take away anything from this guide, let it be these core pillars of a successful options selling strategy:
- Context is King: The "why" behind the trade is as crucial as the "how." Whether it's high implied volatility, an upcoming earnings report, or a strong technical support level, your trade thesis must be clear and well-defined.
- Risk Management is Non-Negotiable: We consistently emphasized defining your maximum loss, calculating your probability of profit (PoP), and ensuring the risk/reward ratio aligns with your strategy. Successful traders manage risk first and let profits follow.
- Strike Selection is a Science and an Art: Your choice of the short and long put strikes directly dictates your premium, your probability of success, and your maximum potential loss. Using tools like delta and probability OTM is the scientific part; understanding the underlying asset's behavior is the art.
Turning Knowledge into Actionable Strategy
Reading through examples is the first step, but a successful trader bridges the gap between theory and execution. Your next objective is to move from passive learning to active application. Don't try to memorize every detail of the MSFT or IWM trade. Instead, internalize the strategic framework used to analyze them.
Your immediate next steps should be to:
- Identify a Potential Setup: Review your watchlist or scan the market for a stock or ETF that mirrors one of the scenarios discussed. Is there a high-IV stock consolidating like our Tesla example? Or a stable index near support like SPY?
- Apply the Framework: Walk through the same analysis we did. Check the implied volatility, identify key support levels, and use delta to select potential strikes. Calculate the max profit, max loss, and break-even price.
- Paper Trade First: Before committing real capital, place the trade in a paper trading account. This allows you to monitor its performance, practice management techniques, and build confidence in your decision-making process without financial risk.
Mastering the credit put spread strategy transforms you from a market spectator into a proactive income generator. It's a method for systematically selling time and probability, creating a consistent cash flow stream from the market's natural movements. By combining the strategic frameworks from each credit put spread example with disciplined execution, you can build a reliable and scalable pillar for your investment portfolio.
Ready to stop guessing and start making data-driven decisions? Strike Price provides the real-time probability metrics and risk analysis tools you need to confidently identify and manage high-probability credit spread trades, just like the examples in this guide. Take the next step in your trading journey and see how our platform can help you find your next winning setup. Learn more at Strike Price.